Forests in the Stuttgart Region are of great importance for the local climate, timber production and local recreation. The forests in the region are used for forestry in suitable locations and contribute to the storage of climate-damaging gases and the formation of fresh air.
Climatic changes mean that the species composition in the forest will change or will have to change. A currently high proportion of non-climate-adapted tree species poses major challenges for forestry. The climate-friendly raw material wood is in high demand, particularly in the energy and raw materials sector. Covering this demand while at the same time climate-induced forest conversion and increasing the carbon storage function poses major challenges for forestry. In addition, forests are becoming increasingly important as balancing bodies in the face of climate change.
Through targeted forest conversion to species- and structure-rich native mixed stands, forestry areas can be developed more closely to nature and thus enhanced. A tree species composition adapted to the location also improves the resilience of the stands to yield-reducing factors such as drought or pests.
Compensation measures on marginal land and special sites can be used to develop rare forest biotope types that provide valuable habitats for flora and fauna. Elements such as forest refugia and habitat tree groups serve as stepping stones and contribute to the networking of near-natural and high-quality forest stands.
Forest landscape model "Sustainable green lung"

The Stuttgart Region has a wide variety of landscapes. One of these is the forest areas. What characterizes the forest today and what would it look like in an ideal-typical state in the future? The document discusses how compensation measures can contribute to achieving the ideal-typical state.
Compensation potential in the forest in the Stuttgart region
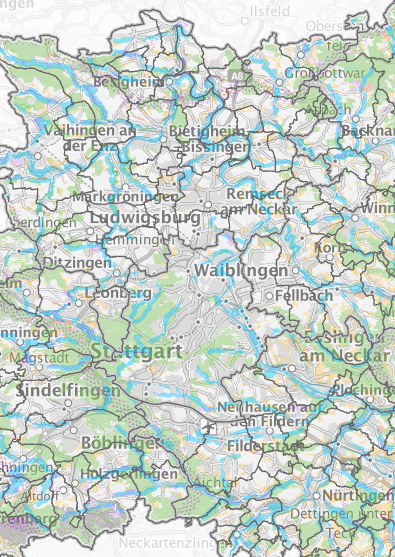
The search area map for the Stuttgart region shows areas where upgrading through compensation measures would be sensible and possible. It also takes forest areas into account. You can find out exactly what a search area map is under Watercourses.
Guidelines for future compensation with added value

How can compensation measures be designed in future so that they are implemented professionally and to the required extent, while at the same time creating benefits for other landscape functions? To this end, three focal points were formulated for possible added value: spatial, functional and procedural. As the central finding of the research project, these free aspects define the framework for action for "compensation with added value".






![[Translate to English:] S-Bahn](/fileadmin/_processed_/3/d/csm_058_-_S-Bahn_Stuttgart_ho___ehengleicher_Einstieg-1-rwilling_ce82cb0b0e.jpg)