Ongoing climate change presents us with major challenges now and in the coming decades. On the one hand, we must continue to work towards minimizing the increase in global warming. The central challenges of climate protection are the energy and mobility transition, i.e. moving away from fossil fuels, the expansion of renewable energy sources and the preservation of green and open spaces as CO2 storage and cooling.
On the other hand, we cannot avoid adapting our living environment to the unavoidable consequences of climate change. Climate adaptation includes, in particular, heavy rain and storm prevention to avoid flooding and storm damage as well as heat and health prevention to protect vulnerable population groups.
Even with intensive efforts to avoid interventions as far as possible, unavoidable interventions will still have to be made in the coming years, for example for the construction of renewable energy plants. Compensation under nature conservation law should then be designed in such a way that it contributes to climate protection and adaptation to climate change.
The "Guidelines for future compensation with added value" developed in the RAMONA project show new ways of planning and implementing compensation measures that also address these two challenges. Multifunctional measures that take various ecosystem services into account achieve several objectives and, for example, fulfill climate protection and nature conservation requirements. If flood protection or erosion control are also taken into account when designing compensation measures, compensation measures can make a sustainable contribution to preventing heavy rainfall and adapting our living environment to climate change. Measures in biotope network systems, both functional and spatial, strengthen migration corridors for endangered animal and plant species, which are more dependent than ever on migration due to changing climate conditions. The bundling of individual measures into large-scale compensation projects increases the chances of the measures lasting in the long term, even in the event of deteriorating climatic conditions, and simplifies maintenance and monitoring.
Forward-looking landscape planning is the fundamental way to plan compensation measures in a climate-resilient manner.
Guidelines for future compensation with added value

How can compensation measures be designed in future so that they are implemented professionally and to the required extent, while at the same time creating benefits for other landscape functions? In response to this question, three focal points for possible added value were formulated: spatial, functional and procedural. As the central finding of the research project, these free aspects define the framework for action for "compensation with added value".
Compensation search area for the Stuttgart region
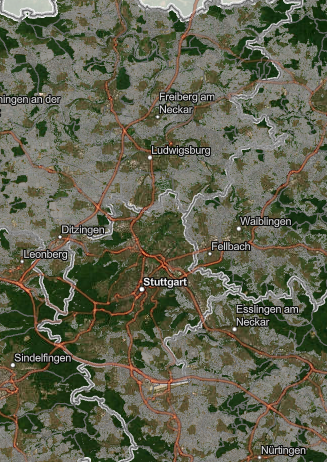
The search area map for the Stuttgart region shows areas where upgrading through compensation measures would be sensible and possible. Through the strategic networking of compensation areas, climate protection and adaptation goals such as water retention and cold air generation can be taken into account.
Policy recommendation for compensation with added value

In the form of nine demands, the policy paper draws attention to current deficits in the compensation process. It shows what political measures are needed to improve offsetting. The recommendations are backed up with examples of pioneering initiatives that illustrate the potential that can be developed and provide information on how the respective approach can be put into practice. The demands made are aimed at political decision-makers at the federal, state and local levels.
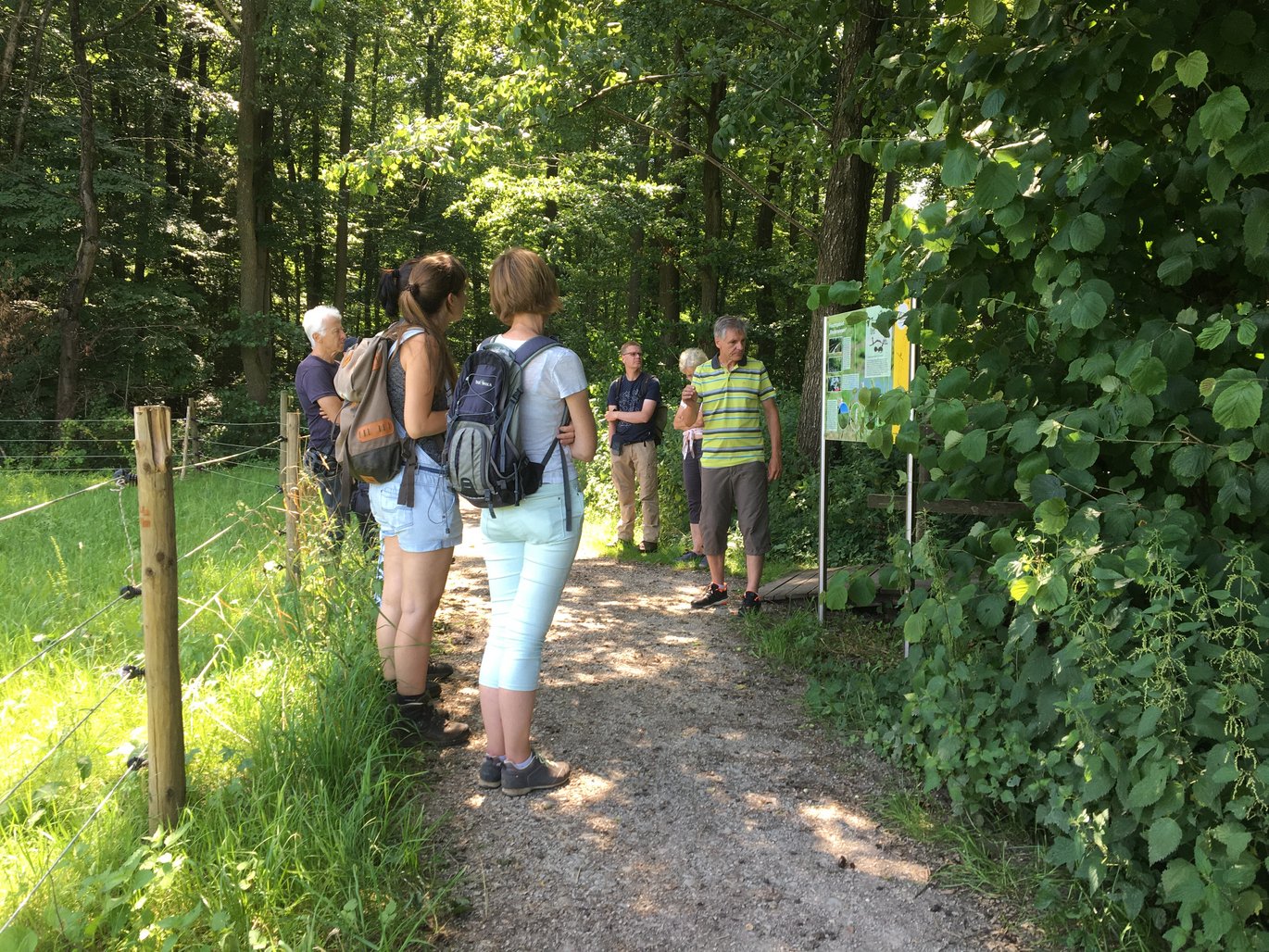
Heavy rain protection in the municipality of Wolfschlugen
In 2008, the municipality of Wolfschlugen was hit by heavy rainfall, which occurs on average every 500-600 years. The municipality, which is located in a hollow, suffered millions in damage to buildings and infrastructure. In order to be better prepared for heavy rain events in the future, the municipality subsequently had a flood protection concept drawn up - with the express aim of not only constructing a technical structure to retain the water, but also combining ecological flood protection that is compatible with the landscape with the creation of local recreational areas. Report from an excursion on site.
Further contents
- Possible solutions for "production-integrated compensation"
- Bundled compensation and inter-municipal coordination
- Providing compensation and strategic land management
- Possibilities for the multifunctional design of compensation measures
- "Compensation measures and then? - Successful implementation of maintenance and monitoring"
- "Landscape plan - the key instrument for planning compensation measures with added value"
- "Production-integrated compensation - a cooperative approach"






![[Translate to English:] S-Bahn](/fileadmin/_processed_/3/d/csm_058_-_S-Bahn_Stuttgart_ho___ehengleicher_Einstieg-1-rwilling_ce82cb0b0e.jpg)